
If anything needs protection, it definitely is endangeredIndia contributes significantly to the global biological diversity. Wildlife diversity is rich in India.
If women in the country are being protected, means there is some danger or risks hampering their lives.
Role of wildlife in maintaining ecological balance:
Our planet's diverse thriving ecosystems may seem like permanent fixtures, but they are actually vulnerable to collapse. Jungle can become deserts and reefs can become lifeless rocks, even without cataclysmic events, like volcanoes and asteroids.
Everyone knows about the process of photosynthesis, where humans and animals both inhale the oxygen released by the plants. Animals help in the dispersal of seeds. Thus making plants and animals both dependent upon each other for their survival. The food chain is the process of maintaining ecological balance as presented in an image below:
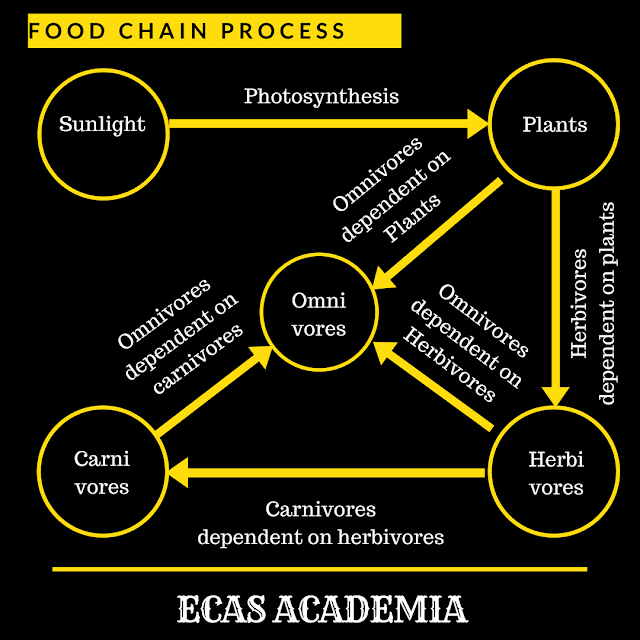
- Sunlight is the main source of energy
- Plants produce food in the presence of sunlight
- Herbivores, like deer and rabbit, feed on the plants
- Carnivores depend upon the flesh of other animals
- Omnivores eat both plants and flesh of other animals
- Thus food chain is formed
Walking through Programmes before Independence:
The programme for wildlife protection started from 1897 with the changes being implemented in the years 1912 and 1919.
During the British Colonial Rule in India, the Britishers were in the slaying habit of getting the raw material at the cheaper rates for modernization and industrialization. The raw material derived from the environment i..e forest; impacted the ecological balance of wildlife preservation.
The wood derived from the forest was used in building the Railway System in India. This process led to the formation of the new term as deforestation; which is now strictly prohibited in the country. The Britishers were now quite aware of the damage that they had made to the environment, so they decided to define the rules in order to protect the environment.
- In 1987, they decided to conserve some key species of flora and fauna.
- In 1912, more species of flora and fauna were included into the programme of protection.
- in 1919, some more species were included.
Then in 1935, the act was passed by British claiming to the need of conservation of wildlife.
The reason was very clear. The first world war was fought to establish the governance and supremacy over the other colonies, for the hunger of industrialization by gaining access to the more cheaper raw material.Western countries were in great demand of the fine raw material found in British India.
This gave the world an alarming message to stop impacting the environment, but "World is Wise".
Extinction of species:
What is extinction? How do the species become extinct?
To extinguish something that needs to stop it from existing. When plant or animal species that once lived stops existing entirely we say that species have become extinct.
Why they extinct? According to the theory of evolution, individual of the same species show some range of variations, some individuals have characteristics that are better suited to their environment making them more likely to survive and reproduce. While others are less well adapted, so they fail to reproduce and their genes are removed from the population. If any species that fail to adapt to the environment or compete with other organisms for the resources and its birth rate is less than the death rate, thus making it extinct. Some man-made developments are also responsible for the extinction of the species.
The human for its generous needs is responsible for the extinction of the species. 99% of the species have been extinct till 2017.
What are these man-made activities?
Imagine a perfect world where humans and animals live in harmony. Now image our world where these species are getting extinct because of our actions.
Habitat Destruction: Humans have been constantly destroying the home of these animals. The trees are being cut or may refer to deforestation; just to get the certain natural resources, room to grow food and room for infrastructure. Why? Because Humans love Money. For the greediness we are destroying our relationship with the other animals, thus we ourselves are responsible for impacting the ecological balance of the environment. Human is now dependent on the environment for the sake of increasing natural resources thus leading to both animal conservation as well as pollution. But here is the problem, human population is rising very fast, for which humans have forced themselves to use the habitats of these animals. If we continue to use their habitats, then these animals can go extinct.
Hunting: Our earlier ancestors lived alongside animals in a mysterious and hostile world. Man's choice was to hunt or go hungry and he had to learn quickly to be a good predator to survive. So human started trapping animals for its need. Somebody needs to remember that 99% of our species have been extinct. The time has arrived when we have to save the world. Why hunting? There are many reasons for hunting which include the hunter-gatherers, these are the people who gather the skins of the animals and sell them into the market for money. The skin of the animals are used in various hand-made items that get the feel of luxury for the money minded people. Hunting has also been the part of history, but now the time has come where we should focus on providing defense for these animals.
Post-Independence of India:
The Stockholm Conference was held in 1972 to conserve the biodiversity by United Nations, then the government of India led by Indira Gandhi became the first country to make constitutional provision, listing it into the 42nd Amendment 1974 of the Constitution of India. There were many principles that were taken care of, during the Stockholm Conference.

These are the list of some Articles and Amendments listed in the Constitution of India, which would rather resolve the one's responsibility in protecting the gems of the environment, otherwise referring to biodiversity. These include:
48-A -> Directive Principle of State Policy, which allowed to hold upon some things which were in shortage, which thus became the responsibility of the State Government. Get to know about judgments to the article

51-A(G)-> Fundamental Duties of the citizen to protect the wildlife. Get to know about judgements to the article

Article 21-> Right to Life providing a clean environment. Get to know about judgments to the article

The law is applicable to all states and Union Terrotories of the country except Jammu and Kashmir



0 comments:
Post a Comment